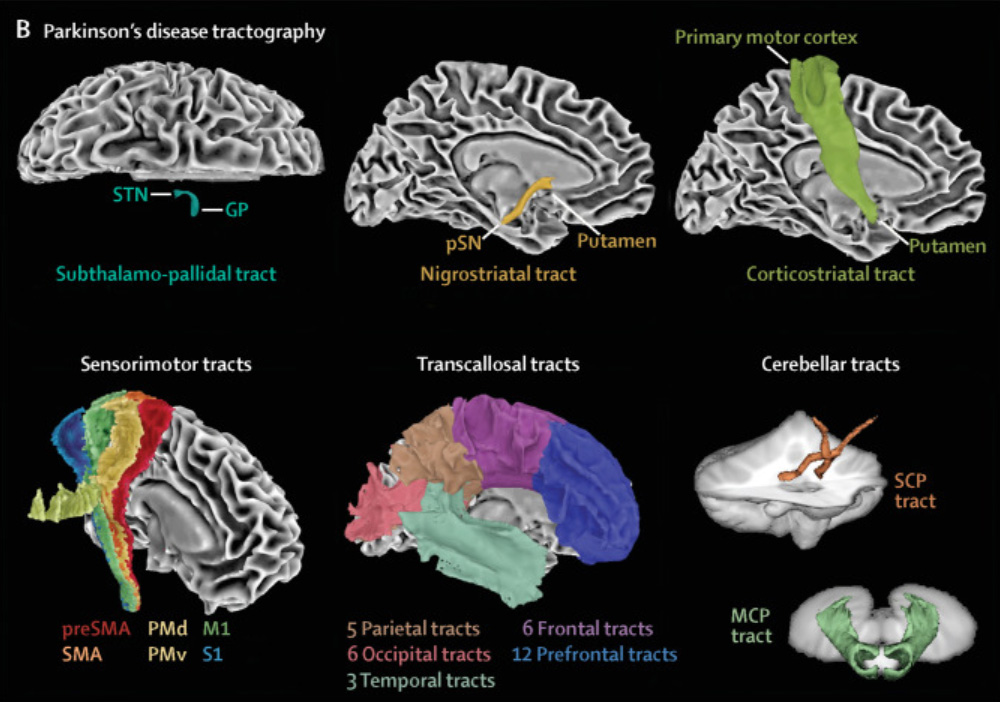
Development and validation of the automated imaging differentiation in parkinsonism (AID-P): a multicentre machine learning study
by Archer, Derek B | Bricker, Justin T | Chu, Winston T | Burciu, Roxana G | McCracken, Johanna L | Lai, Song | Coombes, Stephen A | Fang, Ruogu | Barmpoutis, Angelos | Corcos, Daniel M | Kurani, Ajay S | Mitchell, Trina | Black, Mieniecia L | Herschel, Ellen | Simuni, Tanya | Parrish, Todd B | Comella, Cynthia | Xie, Tao | Seppi, Klaus | Bohnen, Nicolaas I | Müller, Martijn LTM | Albin, Roger L | Krismer, Florian | Du, Guangwei | Lewis, Mechelle M | Huang, Xuemei | Li, Hong | Pasternak, Ofer | McFarland, Nikolaus R | Okun, Michael S | Vaillancourt, David E
The Lancet Digital Health, vol. 1(5), 2019, pp. e222-e231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30105-0
Funded by: National Institutes of Health and Parkinson’s Foundation
The Lancet Digital Health, vol. 1(5), 2019, pp. e222-e231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30105-0
Funded by: National Institutes of Health and Parkinson’s Foundation
Description
Background
Development of valid, non-invasive biomarkers for parkinsonian syndromes is crucially needed. We aimed to assess whether non-invasive diffusion-weighted MRI can distinguish between parkinsonian syndromes using an automated imaging approach.
Methods
We did an international study at 17 MRI centres in Austria, Germany, and the USA. We used diffusion-weighted MRI from 1002 patients and the Movement Disorders Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part III (MDS-UPDRS III) to develop and validate disease-specific machine learning comparisons using 60 template regions and tracts of interest in Montreal Neurological Institute space between Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism (multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy) and between multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. For each comparison, models were developed on a training and validation cohort and evaluated in an independent test cohort by quantifying the area under the curve (AUC) of receiving operating characteristic curves. The primary outcomes were free water and free-water-corrected fractional anisotropy across 60 different template regions.
Findings
In the test cohort for disease-specific comparisons, the diffusion-weighted MRI plus MDS-UPDRS III model (Parkinson’s disease vs atypical parkinsonism had an AUC 0·962; multiple system atrophy vs progressive supranuclear palsy AUC 0·897) and diffusion-weighted MRI only model had high AUCs (Parkinson’s disease vs atypical parkinsonism AUC 0·955; multiple system atrophy vs progressive supranuclear palsy AUC 0·926), whereas the MDS-UPDRS III only models had significantly lower AUCs (Parkinson’s disease vs atypical parkinsonism 0·775; multiple system atrophy vs progressive supranuclear palsy 0·582). These results indicate that a non-invasive imaging approach is capable of differentiating forms of parkinsonism comparable to current gold standard methods.
Interpretations
This study provides an objective, validated, and generalisable imaging approach to distinguish different forms of parkinsonian syndromes using multisite diffusion-weighted MRI cohorts. The diffusion-weighted MRI method does not involve radioactive tracers, is completely automated, and can be collected in less than 12 min across 3T scanners worldwide. The use of this test could positively affect the clinical care of patients with Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism and reduce the number of misdiagnosed cases in clinical trials.
Funding
National Institutes of Health and Parkinson’s Foundation.
Additional information
| Author | Archer, Derek B, Bricker, Justin T, Chu, Winston T, Burciu, Roxana G, McCracken, Johanna L, Lai, Song, Coombes, Stephen A, Fang, Ruogu, Barmpoutis, Angelos, Corcos, Daniel M, Kurani, Ajay S, Mitchell, Trina, Black, Mieniecia L, Herschel, Ellen, Simuni, Tanya, Parrish, Todd B, Comella, Cynthia, Xie, Tao, Seppi, Klaus, Bohnen, Nicolaas I, Müller, Martijn LTM, Albin, Roger L, Krismer, Florian, Du, Guangwei, Lewis, Mechelle M, Huang, Xuemei, Li, Hong, Pasternak, Ofer, McFarland, Nikolaus R, Okun, Michael S, Vaillancourt, David E |
|---|---|
| Journal | The Lancet Digital Health |
| Volume | 1 |
| Number | 5 |
| Year | 2019 |
| Pages | e222-e231 |
| DOI | |
| Funding | National Institutes of Health and Parkinson’s Foundation |
Citation
Citation
Archer, D., Bricker, J., Chu, W., Burciu, R., McCracken, J., Lai, S., Coombes, S., Fang, R., Barmpoutis, A., Corcos, D., Kurani, A., Mitchell, T., Black, M., Herschel, E., Simuni, T., Parrish, T., Comella, C., Xie, T., Seppi, K., Bohnen, N., Müller, M., Albin, R., Krismer, F., Du, G., Lewis, M., Huang, X., Li, H., Pasternak, O., McFarland, N., Okun, M. and Vaillancourt, D., 2019. Development and validation of the automated imaging differentiation in parkinsonism (AID-P): a multicentre machine learning study. The Lancet Digital Health, vol. 1(5), pp. e222-e231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30105-0
BibTex
@article{digitalWorlds:127,
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30105-0},
author = {Archer, Derek B and Bricker, Justin T and Chu, Winston T and Burciu, Roxana G and McCracken, Johanna L and Lai, Song and Coombes, Stephen A and Fang, Ruogu and Barmpoutis, Angelos and Corcos, Daniel M and Kurani, Ajay S and Mitchell, Trina and Black, Mieniecia L and Herschel, Ellen and Simuni, Tanya and Parrish, Todd B and Comella, Cynthia and Xie, Tao and Seppi, Klaus and Bohnen, Nicolaas I and Müller, Martijn LTM and Albin, Roger L and Krismer, Florian and Du, Guangwei and Lewis, Mechelle M and Huang, Xuemei and Li, Hong and Pasternak, Ofer and McFarland, Nikolaus R and Okun, Michael S and Vaillancourt, David E},
title = {Development and validation of the automated imaging differentiation in parkinsonism (AID-P): a multicentre machine learning study},
journal = {The Lancet Digital Health},
volume = {1},
number = {5},
year = {2019},
pages = {e222-e231}
}