Virtual reality and human consciousness: the use of immersive environments in delirium therapy
Technoetic Arts, vol. 16(1), 2018, pp. 75-83. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7571612/
Description
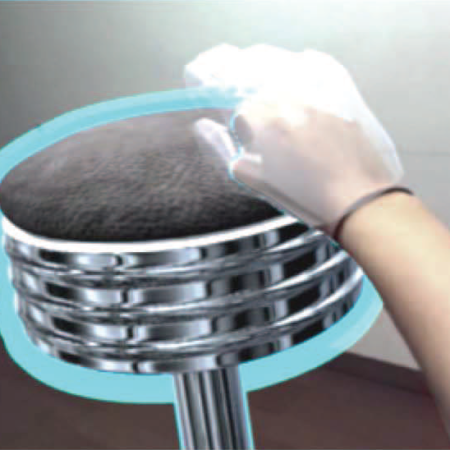
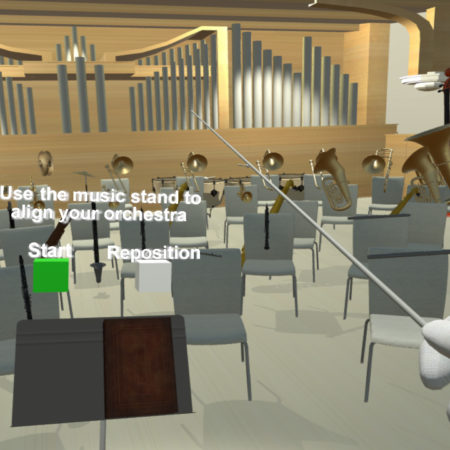
Immersive virtual environments can produce a state of behavior referred to as “presence,” during which the individual responds to the virtual environment as if it were real. Presence can be arranged to scientifically evaluate and affect our consciousness within a controlled virtual environment. This phenomenon makes the use of virtual environments amenable to existing and in-development forms of therapy for various conditions. Delirium in the intensive care unit is one such condition for which virtual reality technology has not been evaluated to date. We are currently assessing the feasibility and utility of a delirium prevention and treatment system which implements virtual reality to improve quality of sleep, reduce pain, lower usage of sedatives, and stimulate cognition. The proposed system will consist of 3-axis wearable accelerometers, 6-DOF position trackers, a virtual reality system, and apps designed to promote sleep quality and mindfulness. Our a priori hypothesis is that our virtual reality therapy system would lower the occurrence of delirium in patients admitted to intensive care units.
Additional information
| Author | Suvajdzic, Marko, Bihorac, Azra, Rashidi, Parisa, Ruppert, Matthew, Williams, Seth, Ozrazgat-Baslanti, Tezcan, Ong,Triton, Appelbaum, Joel |
|---|---|
| Journal | Technoetic Arts |
| Year | 2018 |
| Volume | 16 |
| Number | 1 |
| Pages | 75-83 |
| DOI |
Citation
Citation
BibTex
@article{digitalWorlds:525,
doi = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7571612/},
author = {Suvajdzic, Marko and Bihorac, Azra and Rashidi, Parisa and Ruppert, Matthew and Williams, Seth and Ozrazgat-Baslanti, Tezcan and Ong,Triton and Appelbaum, Joel},
title = {Virtual reality and human consciousness: the use of immersive environments in delirium therapy},
journal = {Technoetic Arts},
volume = {16},
number = {1},
year = {2018},
pages = {75-83}
}